What Is A Composite Material?
Creating new materials with improved properties such as strength, durability or efficiency by combining two or more constituent materials.

What is a composite? – A simple definition
A composite material is a type of material that is created by combining two or more constituent materials with dissimilar chemical or physical properties. In combining these two materials, the resulting composite material will have new properties superior to the original components.
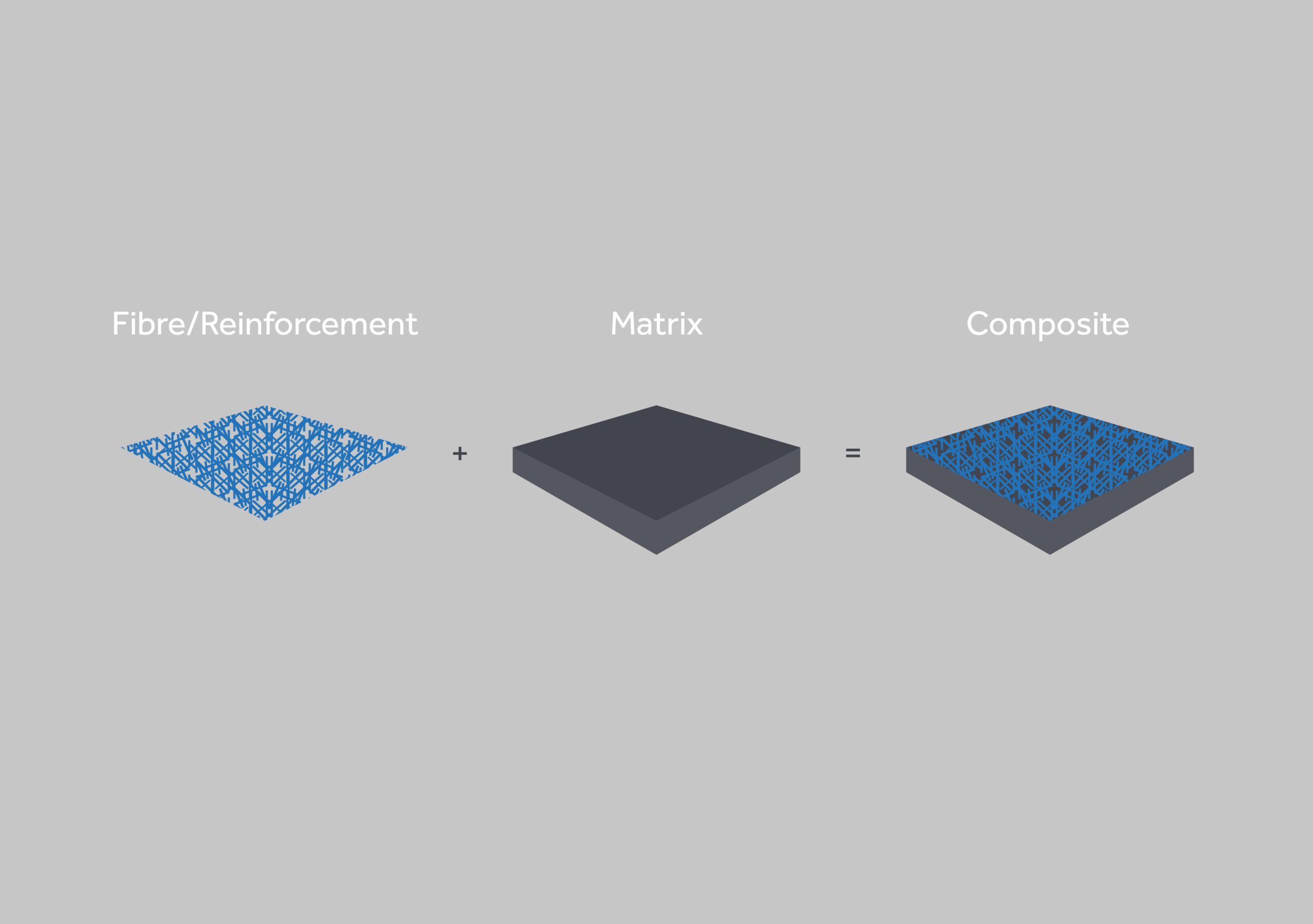
Unlike traditional materials, where the substances are blended or dissolved together, in composites, the individual materials retain their separate identities. One substance, called the matrix, acts as a binder, holding the other substances, called reinforcements or fibres, in place. This unique composition allows composites to possess a combination of properties from the different materials, resulting in enhanced strength, durability, or other desirable characteristics.
Composites diagram- Fibre/Reinforcement + Matrix
The core properties composites are used to enhance
There are a lot of different properties that composites are designed to enhance depending on the desired application. Some of these include:
The benefits of composites
The main benefits of composite materials is of course the enhanced properties that they can offer compared to traditional material which make them the best choice for applications in demanding industries that require properties such as extreme strength or thermal stability. However, this is not the only benefit of these versatile materials. Other advantages include:
What are composite materials used for?
The benefits and enhanced features of composite materials mean their use in a wide range of industries is increasing rapidly, especially as costs and timings are also reducing as the industry itself develops and new learnings are made. From the aerospace industry where composites are employed for aircraft structures, including wings, fuselages, and tail sections, to the automotive industry where composites are used in components such as body panels, chassis parts, and interior elements to enhance strength, reduce weight, and improve safety.
How are composite materials manufactured?
The process for manufacturing composite materials varies based on the type of composite being produced.
Common types of composite materials
There are some common composite materials that are used in all kinds of applications that you have likely already heard of but may not have realised were composites, such as:
Natural and synthetic composites
If we want to be technically correct, we do have to note that composites can be natural or synthetic. Composites do appear in nature (natural composites). For example wood is a natural composite as it is a combination of wood fibres (the reinforcement) and lignin (the matrix) to form the strong material that is wood. The composites we refer to most commonly on this page are synthetic composites as they are man made.
Within synthetic/man-made composites however, you can get two variations again:
Manufacturing parts from composites
Transforming composite materials into composite parts for industries such as defence and marine to use, is a complex process which can involve a lot of different stages. From the part design, to the research and development, manufacture to the testing and quality checks, every composite part will go through a series of stages to be developed and deemed fit for use, and even then, most parts are continually being tested and optimised for their dedicated purpose. Many companies and industries will select a dedicated composites manufacturing company to create the composite parts they require. At Piran Composites, we provide a complete end-to-end solution for our customers, covering all areas of composite part manufacturing for all major OEMs, however, other composite companies may choose to specialise in particular composite capabilities.
The history of composite materials
The use of composites has a fascinating history that dates back thousands of years. Surprisingly, evidence of composite materials can be traced as far back as 3400 B.C., with the Mesopotamians glueing wood strips together to create plywood. The Egyptians also embraced composites, using linen and plaster to make death masks around 2181 B.C., and incorporating straw to reinforce mud bricks and pottery by 1500 B.C.
As societies progressed, so did the use of composites. In approximately 1200 A.D., the Mongols skillfully crafted composite bows by combining wood, bamboo, bone, cattle tendons, and silk, enhancing their accuracy with natural pine resins. However, it was the 1870s that marked a significant turning point. With the development of polymers, plastics began to emerge, and by 1930, glass fibres were created.
The momentum of composite materials accelerated during World War II when they proved instrumental in constructing boat hulls and radar systems. From there, their prominence continued to grow, culminating in the mid-1990s when composites became the norm in mainstream manufacturing, a status they maintain today. The evolution of composites showcases their enduring importance and their journey from ancient glueing techniques to cutting-edge advancements in modern technology.

The future of composites
With ongoing research and development, new materials and manufacturing techniques continue to emerge, pushing the boundaries of what composites can achieve. The focus lies in enhancing the performance, durability, and sustainability of composite materials. Innovations include the exploration of nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical properties, the development of bio-based and recycled composite materials for reduced environmental impact, and the integration of sensors and smart functionalities into composites for structural health monitoring.
As we look towards a future driven by technological advancements and the imperative for sustainability, composites can and will play a key role in this. From providing structural elements for hydrogen or battery storage to opening new opportunities for the renewable sector, as technology advances, the future of composites promises exciting possibilities, enabling lighter, stronger, and more efficient solutions in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, renewable energy, and infrastructure.
Unsure if composites could be the solution you’re looking for?
Discover if composite materials and parts could help your business grow and develop. Speak to a composites expert today.
Composite Material FAQs
Are composites just plastics?
No, composites are not just plastics. While some composites use polymers as the matrix material, composites can also include other materials like metals, ceramics, or natural fibres.
What are the four primary categories of composite materials?
The four primary categories of composite materials are polymer matrix composites (PMCs), metal matrix composites (MMCs), ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), and carbon matrix composites (CMCs).
Are composite materials more expensive than traditional materials?
Composite materials can vary in cost depending on factors such as the specific materials used, manufacturing processes, and application requirements. In some cases, composites can be more expensive than traditional materials, while in others, they can offer cost savings due to factors like reduced weight, increased durability, or improved performance.
What are the common matrix materials used in composites?
Common matrix materials used in composites include polymers (such as epoxy, polyester, or vinyl ester), metals (such as aluminum or titanium), ceramics (such as silicon carbide or alumina), and carbon.
What are composites not?
Composites are not made by dissolving or blending materials together.
Are composite materials environmentally friendly?
Composite materials can be environmentally friendly depending on their composition and end-of-life considerations. Some composite materials can be recycled, while others may pose challenges due to the combination of different materials. Ongoing research focuses on developing sustainable and recyclable composite materials.
Are there any limitations to using composite materials?
Like all things, composite materials have limitations. These can include issues such as susceptibility to delamination, lower impact resistance compared to metals, difficulties in repair and maintenance, and higher manufacturing complexity for certain applications. A good composite manufacturer will consider these and discuss any limitations with you.
What are the common fibre materials used in composites?
Common fibre materials used in composites include carbon fibres, glass fibres, aramid fibres (such as Kevlar), natural fibres (such as flax or hemp), and metal fibres (such as steel or aluminum).
